

Speed refers to the quantitative measurement of how swiftly something moves.Ī moving entity's speed can never be negative. Velocity of a body or an object determines its movement direction. We can now see that, even if the car's speed varies, if it covers the same amount of distance in the same amount of time, its average velocity remains constant.
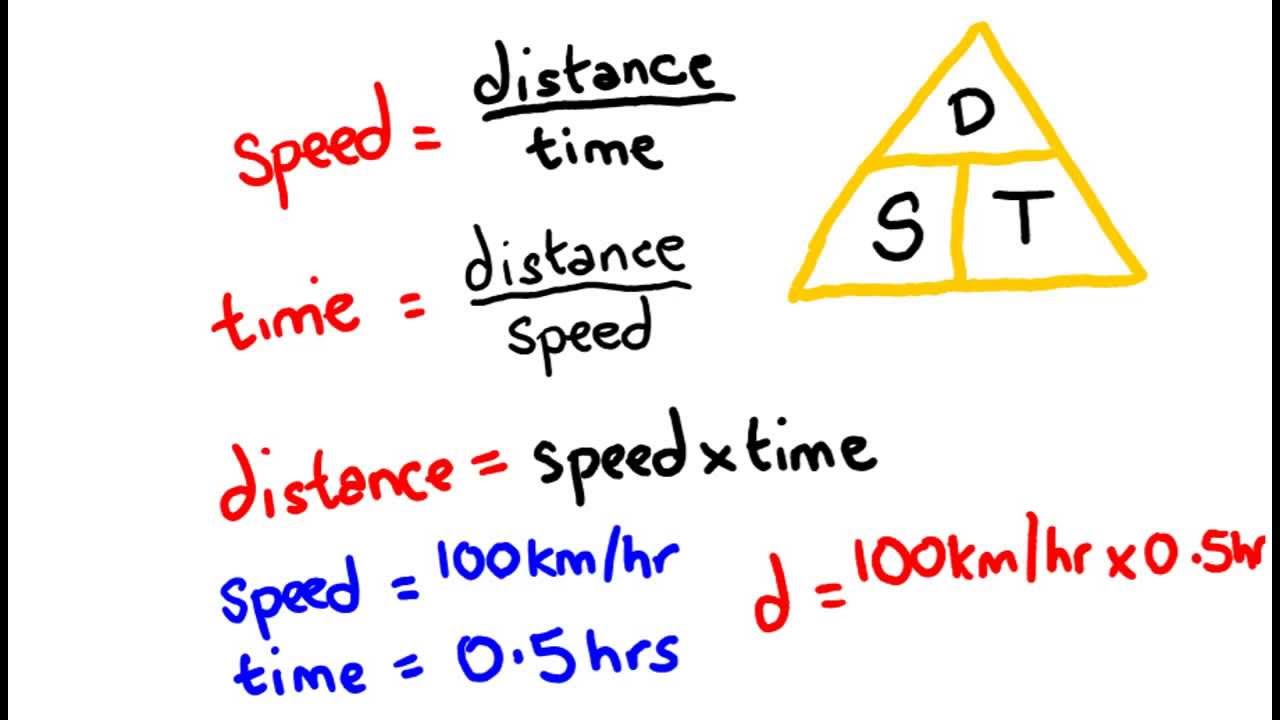
As a result, 20 minutes equals 0.33 hours. We've assumed the car is moving in a straight line for simplicity's sake, and we'll convert all time units to hours. So, here's how we figure out what Shweta's car's average speed is: Her school is 10 kilometres away, and it takes her 20 minutes to get there, but the speedometer on the dashboard of her automobile always shows a different value. Let's look at an example to help you grasp the difference between instantaneous and average velocity.Įvery morning, Shweta rides in her mother's car to school. Relation Between Torque and Moment of Inertia Average speed is always less than or equal to average velocity this is because, displacement can never exceed the distance travelled, yet the distance travelled can exceed displacement.The average velocity is calculated by multiplying the total displacement by the entire time, v = xt, where x is the total displacement of the body and t is the time.Velocity of a body at any particular time is known as instantaneous velocity.Velocity is a function of displacement, whereas speed is a function of distance travelled.The variation between speed and velocity is that speed informs us how rapidly an object is going, but velocity tells us not only how fast an object is moving but also in which direction it is travelling.Here, we explain how both concepts are different. At that point, the magnitude of the instantaneous velocity equals the instantaneous speed.įor most of us, the concepts of speed and velocity are a little puzzling. When an object's instantaneous velocity is measured, it tells us how fast it moves at different places in a specific time interval. The magnitude of velocity is the speed at which something happens right now. Meaning that in equal intervals of time, the average velocity remains constant. Assuming that a body falls under gravity with terminal velocity, what happens to the average velocity?Īns. Assuming that a body falls under gravity, the velocity does not vary when the body moves with terminal velocity. Hence, the average speed = 200/4 = 50 km/hr. Ques 1. In order to complete a journey of 200 km, a truck needs at least 4 hrs, thus calculate its average speed.Įxplanation: Average speed = total distance/total time taken. Therefore, the rate of change of tangential velocity somewhere in a circular orbit is called tangential acceleration.Questions Related to Average Velocity and Speed It remains perpendicular to the centripetal acceleration at that time. Tangential Acceleration is the rate of change of speed in an area where indirect movement occurs. It is expressed in metre per second (m/s). The given formula is applied in calculating the tangential velocity of any object moving in a circular path. Where, r is the radius of the circular path and ω is the angular velocity. Tangential Velocity formula is mathematically represented as, We can hence say that the object possesses angular velocity as it rotates in a circular motion with a certain number of radians per second.Ĭircular Motion of Object and Tangential Velocity From the top to the bottom, the object is just a circle, and the string is the width of that circle. An object cannot go farther than the length of the thread, so if it continues in a constant motion, its movement will be circular. Imagine a small object tied to a rope, around a fixed place. Tangential velocity can be defined as the linear component of a moving object in circular motion.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
